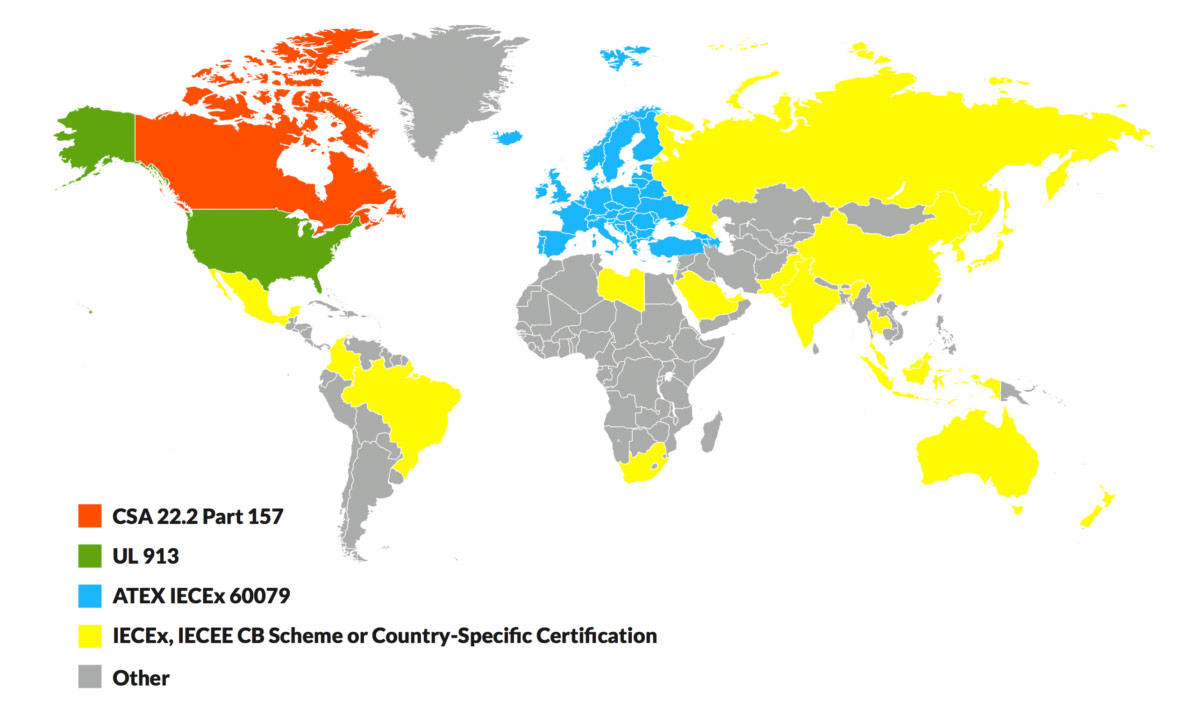
Intrinsically Safe Devices
Workforces operating in the world’s most hazardous environments require mobile communications devices that can be used without the risk of causing an explosion. The Aegex platform includes devices that are Intrinsically Safe (IS) - incapable of creating enough heat or a spark sufficient to ignite the work environment.
Aegex IS devices are purpose-built for explosive environments, meaning their configuration makes impossible the generation of heat sufficient for ignition. Our IS devices are certified ATEX Zone 1, IECEx Zone 1 and Class I, II, III Division 1. Users in critical zones of operation can work safely and efficiently without worrying that their Aegex communication device will cause an explosion.